18.2 What’s driving globalisation?
National comparative advantage
Due to differences in the amount, types and quality of their economic resources, some countries have a natural advantage in production of specific products; this advantage is known as the national comparative advantage. Australia, for example, is able to produce farm commodities such as wheat and fine wool at a lower cost and higher quality than other nations. Similarly, many Southeast Asian nations have access to a large pool of labour at a lower cost than Australia. This gives them a comparative advantage in the production of manufactured items like clothing and footwear. When nations specialise in production of a smaller number of products they develop a comparative advantage.
Reduced transport costs
Reduced costs have come from advances in transport technologies. The introduction of containerisation and other innovations has facilitated reduced shipping costs. It is now much cheaper to import and export.
| Date | Number of users | % world population | Information source |
|---|---|---|---|
| December 1995 | 16 million | 0.4% | IDC |
| December 2000 | 361 million | 5.8% | Internet World Stats |
| December 2005 | 1018 million | 15.7% | Internet World Stats |
| September 2010 | 1971 million | 28.8% | Internet World Stats |
| December 2011 | 2267 million | 32.7% | Internet World Stats |
| December 2012 | 2497 million | 35.7% | ITU |
| March 2014 (estimate) | 2937 million | 40.7% | Internet World Stats |
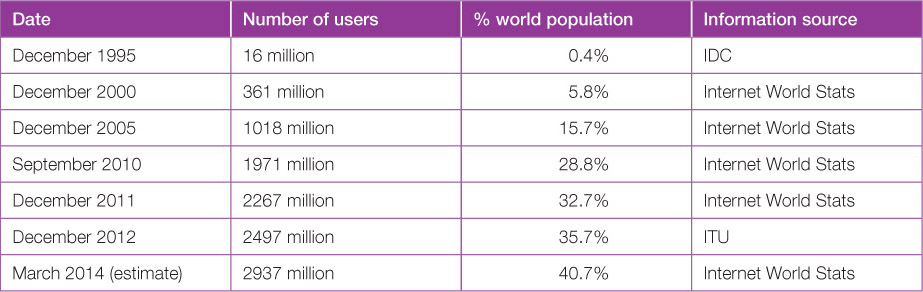
Communications development
It is now easier to communicate with the world. The cost of a 3-minute phone call to Europe from Australia has fallen in real terms from $350 in 1926 to less than $1 in 2014. It is now possible to trade and communicate instantly and cheaply due to the development of the internet.

Removal of trade barriers
Governments have reduced barriers to trade like tariffs and import quotas. As a result it is easier to trade with other nations and imported items have become cheaper in comparison to locally produced products. Governments have also encouraged the development of the global economy through forming free trade agreements between nations.
