8.1 What is ICT?
Information and communications technologies (ICTs) are the tools that help us connect with each other. At a local scale this may involve linking computers in a school or accessing the global community using the internet.
The internet and the World Wide Web (WWW) are not the same thing. The internet is all the networks of computers that are linked together; the World Wide Web is the linked pages that are accessed using the internet and web browsers. The internet combined with the World Wide Web enables file sharing, social networking, gaming, research, email, telephone and video calls, and more.

Information
Information must be meaningful to people. The presentation method chosen will vary depending on factors such as age, educational level and cultural background. For example, a table of statistics about internet use around the world may be easier to interpret if it is presented as a graph or map.
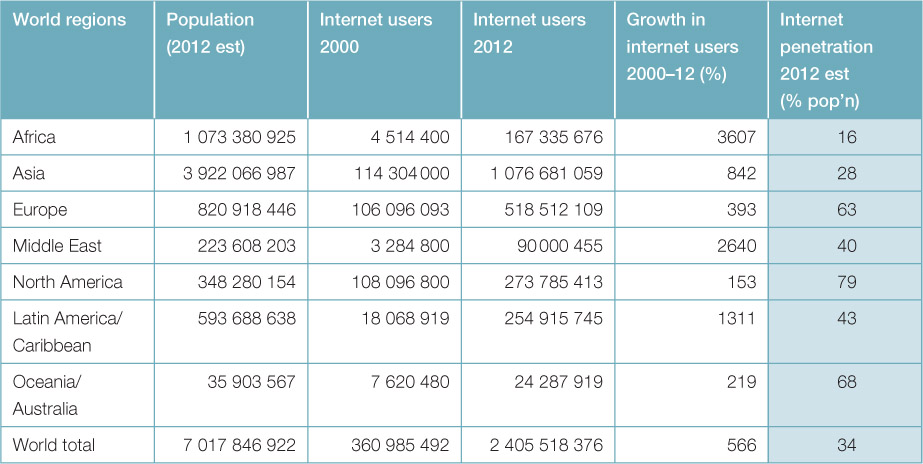
| World regions | Population (2012est) | Internet users 2000 | Internet users 2012 | Growth in internet users 2000–12 (%) | Internet penetration 2012 est (% pop'n) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Africa | 1 073 380 925 | 4 514 400 | 167 335 676 | 3607 | 16 |
| Asia | 3 922 066 987 | 114 304 000 | 1 076 681 059 | 842 | 28 |
| Europe | 820 918 446 | 106 096 093 | 518 512 109 | 393 | 63 |
| Middle East | 223 608 203 | 3 284 800 | 90 000 455 | 2640 | 40 |
| North America | 348 280 154 | 108 096 800 | 273 785 413 | 153 | 79 |
| Latin America/ Caribbean | 593 688 638 | 18 068 919 | 254 915 745 | 1311 | 43 |
| Oceania/ Australia | 35 903 567 | 7 620 480 | 24 287 919 | 219 | 68 |
| World total | 7 017 846 922 | 360 985 492 | 2 405 518 376 | 566 | 34 |
Communications technologies
Communication involves the transfer of information using technologies or tools. In order to connect to the internet, infrastructure is needed – it may include cable, wireless, microwave or satellite technologies.
DEVELOPING YOUR UNDERSTANDING 8.1
Refer to Source 8.2 for Questions 1 to 3.
- Name the region with the largest number of internet users and the one with the smallest.
- Explain how the internet penetration figures are calculated.
- Compare the number of internet users with the internet penetration figures.
- Discuss which information source – Source 8.2 or Source 8.3 – is easier to understand. Suggest reasons.
Benefits of ICT
In general, the aims of using ICT are to complete tasks better, faster and with less effort. Predictions suggest that existing technologies will continue to merge, in the same way that the telephone and internet access have merged using mobile phone technology.
Global use of ICT
Change in the field of ICT is rapid and ongoing.
According to the Secretary-General of the United Nations International Telecommunications Union, the number of internet users increased from 250 million in 2000 to 2.1 billion in 2011. The number of mobile phone subscriptions has also increased globally from 500 million in 2000 to an estimated 5.28 billion in 2011.
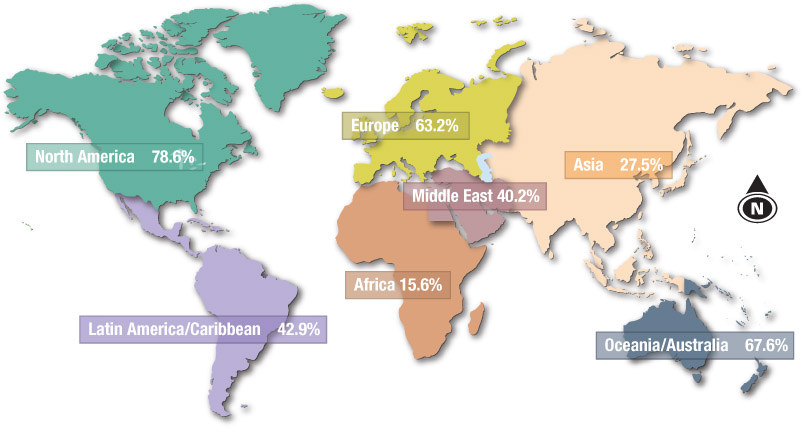
The digital divide refers to variations in access to the internet between and within countries.
It is generally believed that access to the internet varies both within countries (especially between rural and urban regions) and between countries according to their level of economic development.
Any reference to a digital divide should also consider other factors that affect the provision and use of ICT, such as cost, speed and quality of internet connections, personal skills, maintenance of equipment, privacy issues and the threats of computer viruses.
Analysing spatial data using interactive mapping
Go to www.cambridge.edu.au/hass9weblinks and follow the link to the website IndexMundi. It gives access to statistics, graphs and mapped data about many countries worldwide. The site collects data from many sources and allows users to explore those data at a global, regional and country scale.
The following activities relate to ICT and mobile phone usage in Africa. There are other development indicators, such as electricity consumption per capita or GDP per capita, on the site that you may wish to explore. Purchasing power parity (PPP) allows international comparisons to be made: it is a conversion factor for calculating how much foreign money would be needed to buy the same goods or services in the US market.

DEVELOPING YOUR UNDERSTANDING 8.2
- Define PPP (purchasing power parity).
- List the problems associated with interpreting statistics relating to the internet.
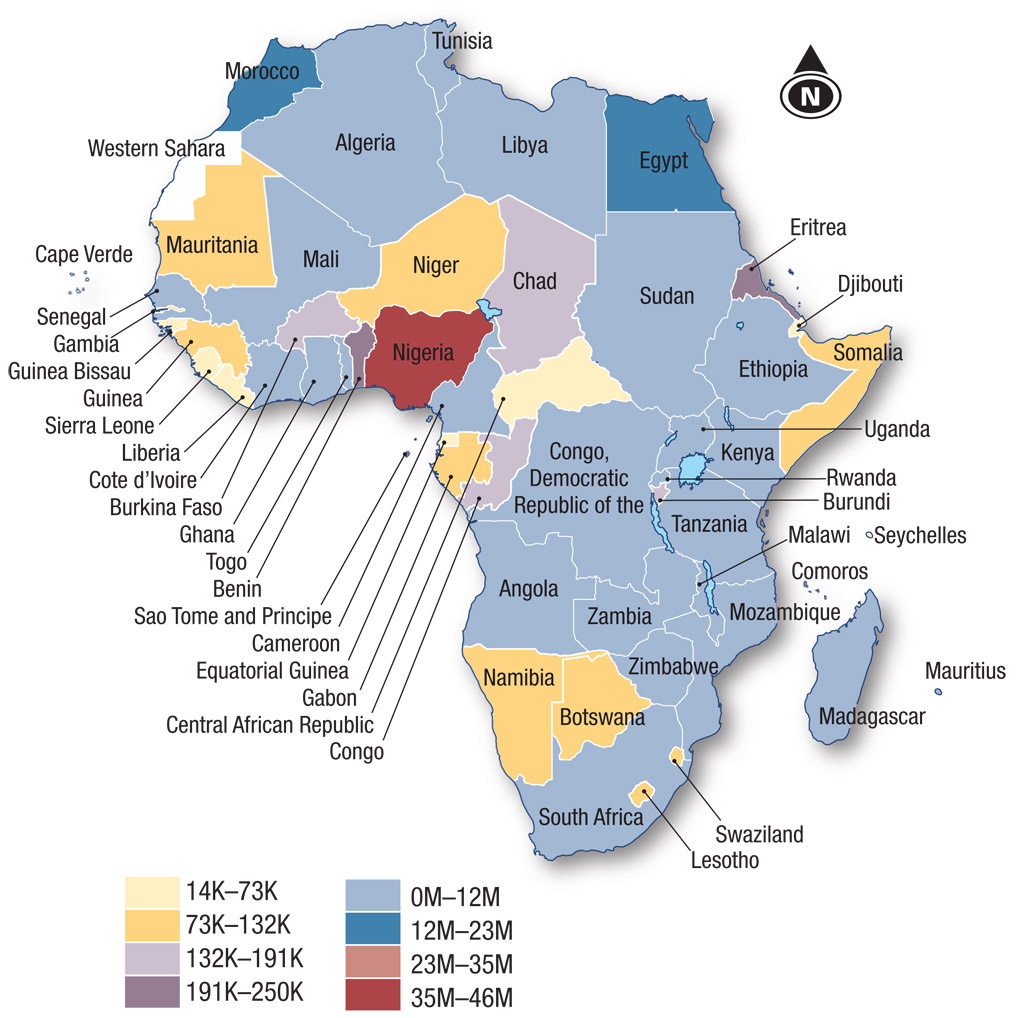
- Describe the distribution of internet users in Source 8.6:
- general trend
- examples
- exceptions.
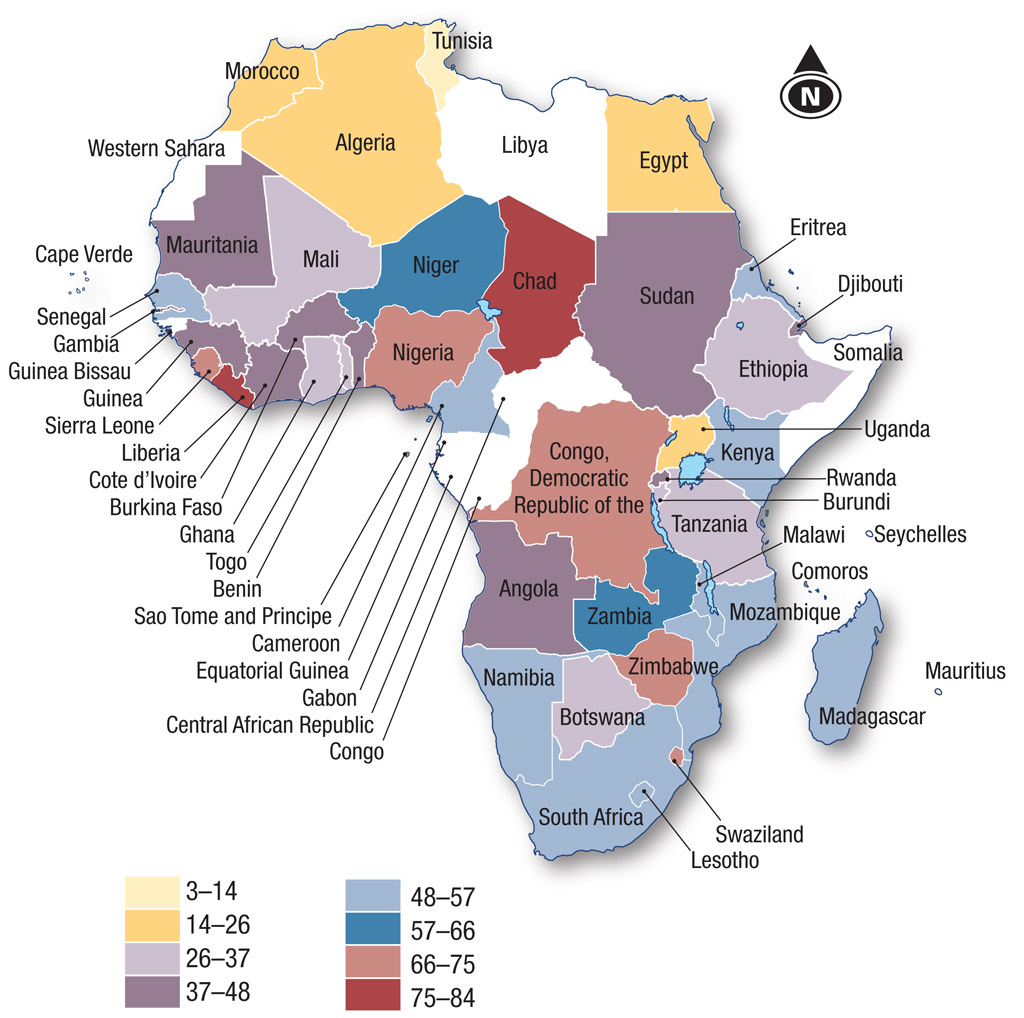
- Describe the spatial association between the distribution of internet users in Source 8.6 and population below the poverty line in Source 8.7.
- From the evidence suggested in these maps and your investigation of the websites for IndexMundi and the World Bank (follow the link to these through www.cambridge.edu.au/ hass9weblinks), to what degree does ICT correlate with other economic development indicators across Africa?
- What does ‘per capita’ mean?
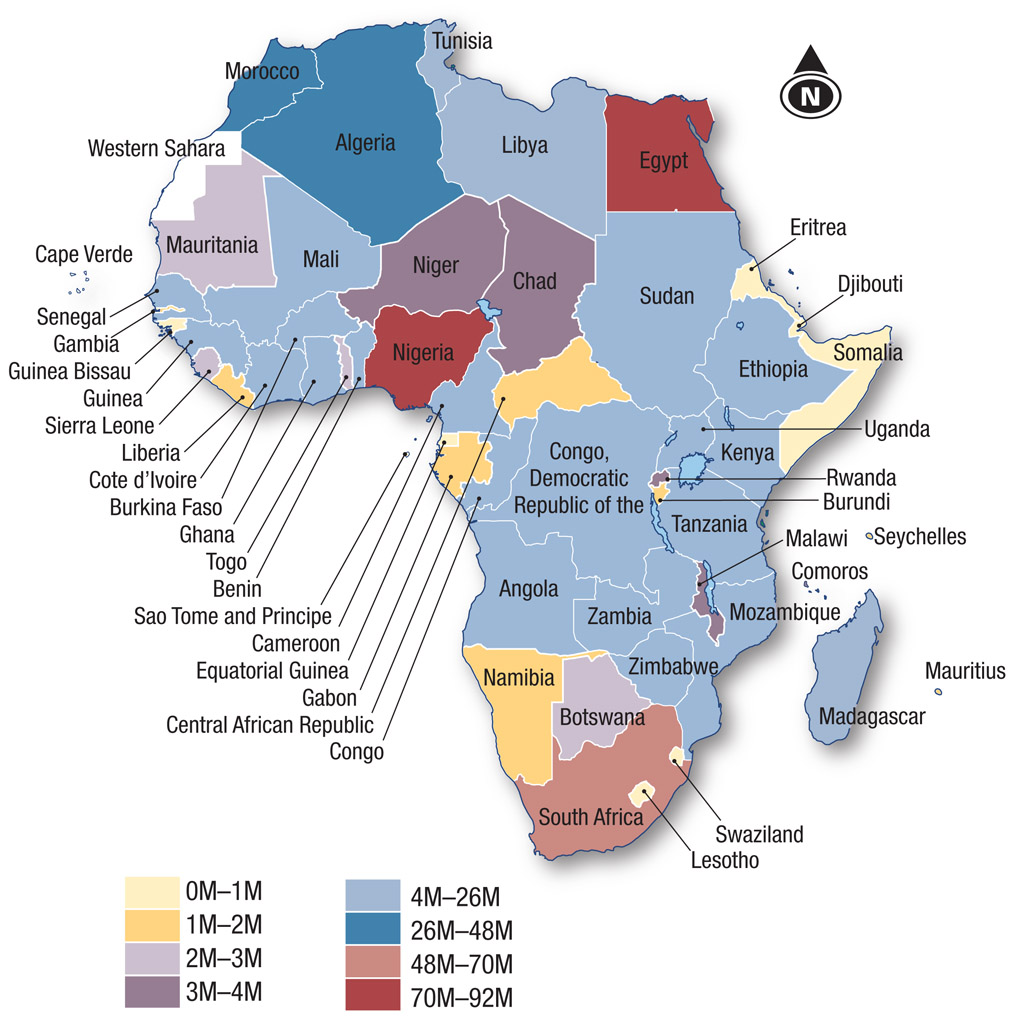
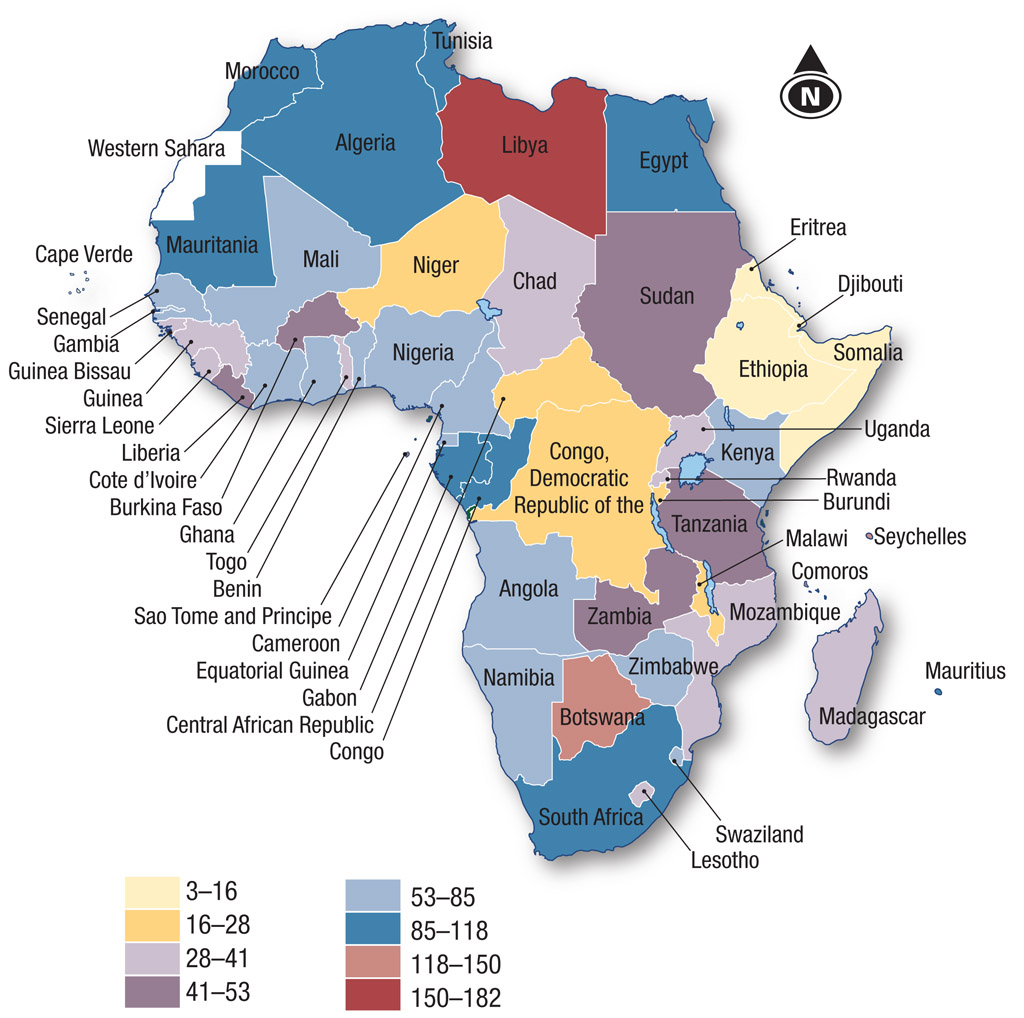
- Compare Sources 8.8 and 8.9, which show the pattern of mobile use and mobile phone lines per 100 people in Africa.
Cloud computing – helping to overcome ICT barriers
Recent developments, including cloud computing, may provide opportunities for less economically developed regions to access software and services (such as data storage, applications or file sharing) via the internet and help countries become less reliant on physical infrastructure.