6.3 Where your laptop comes from
As this chapter has explored, where products are manufactured and sold is a complex and everchanging story. An excellent example of these complexities revolves around where a laptop is produced. This product is likely to have been designed and manufactured in lots of different countries.
-
Design
Your laptop, if it is made by a company such as HP or Apple, is likely to have been designed in Silicon Valley. These companies keep processes such as designing and research and development in these types of regions to take advantage of the expertise and skills of the workers there.
-

-
Sourcing of raw materials
Many parts in your computer are made from silicon chips. Silica for this purpose is mined in a variety of locations, including Nevada in the United States. Other raw materials required may include rubber for keys, which may come from Brazil or Malaysia, as well as copper and other metals. Copper from this mine at Mt Isa may make its way into your laptop.
-

-
Manufacturing of components
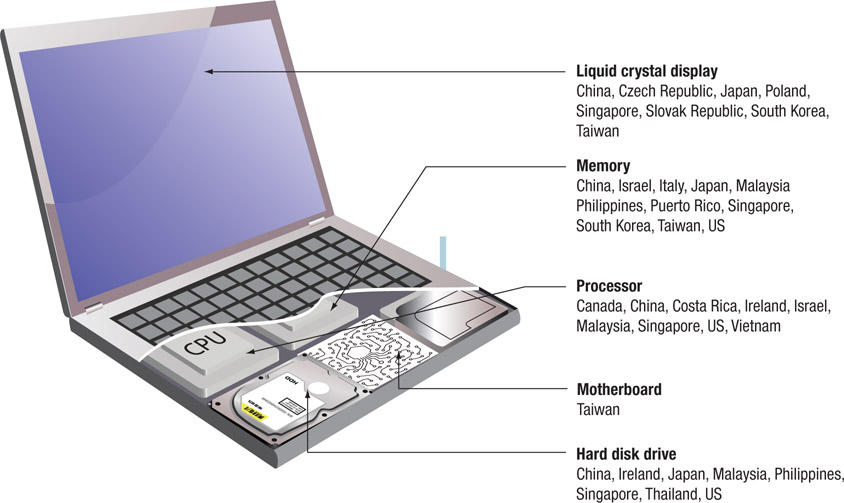
A laptop has up to 30 components. These components are likely to be made in a wide range of countries.
The country of origin is usually dictated by how advanced the manufacturing process is. So some complex items, such as the main CPU, are probably still manufactured in the United States, South Korea or Taiwan, although new hi-tech factories are being built in Southeast Asia. Other items, such as keys, are likely to be pressed out in huge volumes in factories in China, or in countries with low labour costs, such as the Philippines or Thailand.
-
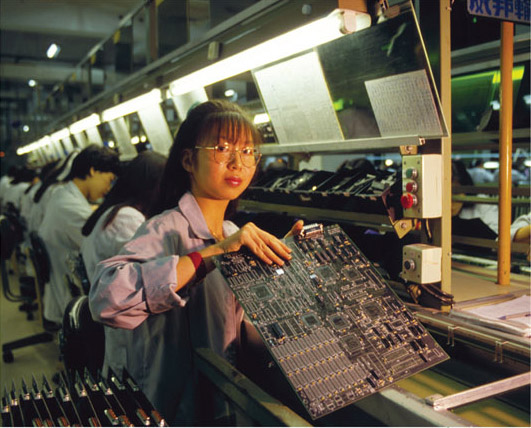
Assembling the laptop
Chinese factories assemble 70% of the world’s laptops. While some companies, such as Toshiba, have their own factories, most businesses outsource their assembly lines to companies in China. Many of these assembly lines will be producing computers for a number of companies at the same time. These factories are likely to be near ports and airports so that components can be shipped in and laptops shipped or flown out.
Selling laptops
Until recently, laptops may have been assembled in China but sold through retail outlets all over the world. Advances in communication and technology are now allowing companies to bypass this process, and sell direct to the consumer. As the diagram above illustrates, computers can be ordered in the finding an external company or worker to produce a product in part or in whole, custom-built in Shanghai with the desired components, and shipped out directly to the customer within 24 hours. This type of process maximises profits for the computer companies, as they cut the retail step out of their costs, while increasing convenience for the consumer. It has, however, affected physical computer shops, which are struggling to compete with the computer companies because of their overheads – such as rent and staff. People are becoming more comfortable buying expensive goods over the internet, so this change in business practice is likely to accelerate.
DEVELOPING YOUR UNDERSTANDING 6.6
- Explain why computers are still designed in countries such as the United States.
- List the steps in the designing, making and assembling of a laptop and then compare the levels of technology required for each step.
- Discuss why computer companies outsource the assembly of their laptops.
- Create a map of the country of origin for the computer parts used in the HP laptop.
