1.4 The sun and the biotic environment: flora and fauna
Sunlight generates the process of photosynthesis in plants. This process is essential for much of life on Earth. Photosynthesis is a complex chemical process, involving chlorophyll, carbon dioxide, water and sunlight, and produces the carbon and sugar compounds necessary for plant growth and the release of oxygen so necessary for animal life (including human life) on the planet.
Plants have a number of roles in ecosystems.
Some plants provide shade in which other plants will grow. Some plants are hosts for other plants; climbers and epiphytes, for example, need host plants. Many plants have special adaptations that allow them to grow in specific areas (mangroves and cacti, for example). All plants die, and in death they decompose and provide food for other plants.
Around the world there are some very difficult areas for plants to colonise. The growth of plants in these areas requires colonising plants with very special adaptations. These plants stabilise the environment and allow other plants, plants that are not adapted to the initial conditions, to eventually move into an area.
DEVELOPING YOUR UNDERSTANDING 1.1
Source 1.4l Transition from bare ground to a forest cover (01:16)
The first plants to inhabit an area are known as the colonisers.
The role of the colonisers is to establish an environment which will allow other plants to grow. The colonisers help break down the rock into soil, and when they die they provide plant nutrients for a later group of plants. Eventually the environment is changed significantly by different groups of plants. A soil layer is developed and larger plants then provide protection for seedlings of still larger plants. The most dominant form of vegetation in an area is known as the climax vegetation. Climax vegetation is the major plant community that will develop in an area given the existing climatic conditions.
For a large part of eastern Australia, the climax vegetation is eucalypt forest. Don’t lose sight of the fact that it is the sun that is driving this vegetation development.
The animal kingdom is affected by sunlight in two ways. The time of day can have a significant effect on when animals are active. Some are diurnal. These animals are active during the day: giraffes and wildebeest, for example, are diurnal. Some are nocturnal. These are active at night: owls and flying foxes, for example, are nocturnal. Some are crepuscular. These are active in the twilight hours of early morning and early evening: many birds, for instance, use these hours to visit water sources. Deer, too, are most active in the twilight hours.
Interactive 1.2
The other way sunlight affects the animal kingdom is through its effect on vegetation.
There are animals which only eat plant material. These are the primary producers in an ecosystem. Primary producers can be as small as caterpillars and as large as giraffes. They convert plant material into the food needed for their survival.
They also produce waste products, in the form of gases, solids and liquids, which assist in the breakdown of plant material. On a more important level, many primary producer animals are the food of the next level of animals in the food chain – the carnivores.
These animals eat other animals.
Source 1.5 is a simple version of what happens in many parts of the world. The sun provides the necessities for plant growth. A herbivore grazes on the plants and a carnivore consumes the herbivore.
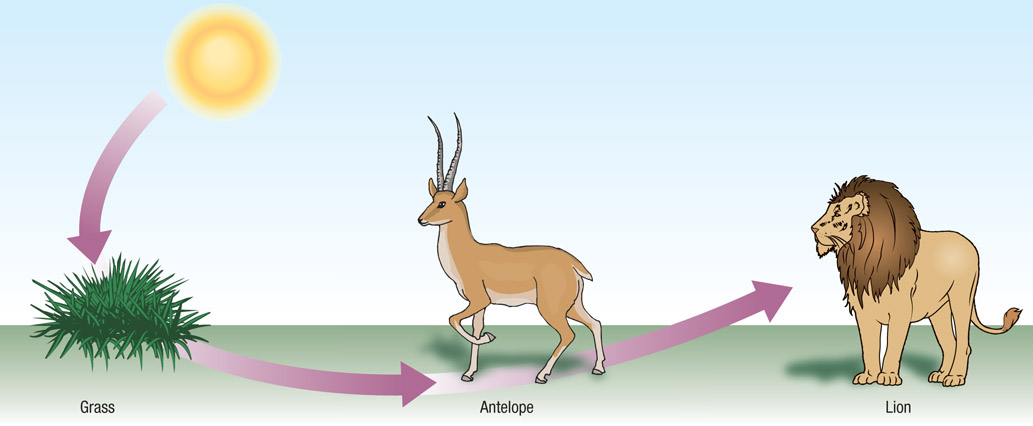
The actual situation is not that simple. The study of biomes in the next chapter will investigate the relationships between plants, animals and the environment in more detail.
The interesting thing about human beings is that they have an increased ability to survive because they consume all levels of the food chain, from the plants at the base (such as carrots, tomatoes and peas) to the herbivores (cows, antelopes, kangaroos) to the carnivores (sharks, crocodiles).
The role of the sun’s energy in relation to plant and animal life on Earth is not over even when plants and animals die. Many of the wastes remaining when a plant or animal dies go through further processing to return their nutrients to the environment. This is where the decomposers come in. They break down the decaying life form into nutrients which can be used again in the ecosystem.
Scavengers form part of this group. Crows, Tasmanian devils and hyenas are scavengers. (Hyenas also hunt.) Fungi and bacteria are other life forms that assist in the decomposition of plant and animal remains.